Hyperrealism painting and drawing
Hyperrealism Paintings: Extreme Realism
Hyperrealism, also referred to as photorealism, is an artistic style that captures subjects in a strikingly authentic and lifelike manner through painting and sculpture. This meticulous approach showcases an intense focus on small details and employs photographic methods to achieve its realistic vision.
In the mid-1960s, a group of talented American artists began painting from photographs with intricate detail, thus sparking a revolutionary movement that has since captured the hearts of art lovers around the world. Called Hyperrealism, the movement has carved a unique niche for itself in the art world, gaining widespread acclaim for its relatable aesthetic.
Hyperrealism, Photorealism, and Superrealism are terms associated with this style. The images used by hyperrealists for their paintings were high-quality photographs taken with hyper realistic cameras. These cameras were capable of capturing details that the human eye couldn't perceive in its normal state. The painter, with impeccable technique and great precision, depicted these photographs in such a realistic manner that it left the viewer astonished.
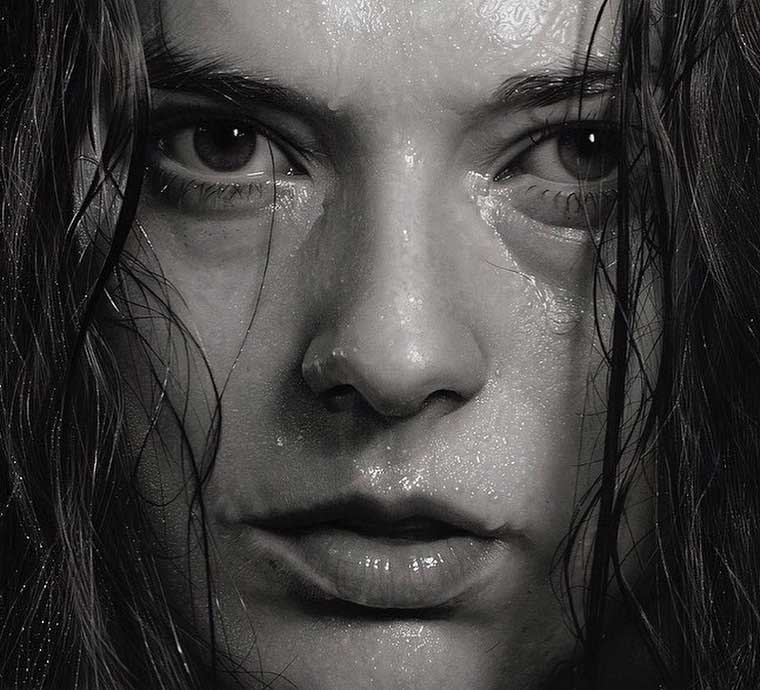

A Hyperrealism Painting by Dirk Dzimirsky
Hyperrealist artists must possess a high level of technique and skill in order to engage the viewer with a world that is more real than reality itself by understanding and presenting various complex levels of reality. For this reason, and due to the importance of technique among hyperrealist painters, the evaluation and critique of hyper realistic works have always been contentious in terms of technique. Unfortunately, the lack of recognition for the significance of technique has often led to incorrect judgments about these artists.
History and Introduction of Hyperrealist Painters:
First Generation of Photorealist Painters
The first generation of hyper realist painters emerged in the early 1960s and included artists such as Chuck Close, Robert Bechtle, Richard Estes, Audrey Flack, Tom Blackwell, Ron Kleemann, Don Eddy, Robert Cottingham, Charles Bell, Ralph Goings, John Baeder, Ben Schonzeit, Jack Mendenhall and John Salt. John Salt was the only non-American artist in the group and was British. Many hyperrealist and photorealist artists also engaged in photography and worked as realist photographers. Chuck Close, for example, is considered one of the founders of the 1960s American Photorealist photographers due to his unique style of portrait photography. In general, the subjects of hyperrealist and photorealist paintings consisted of American lifestyle, the appearance of machine-driven culture and modern capitalist society.
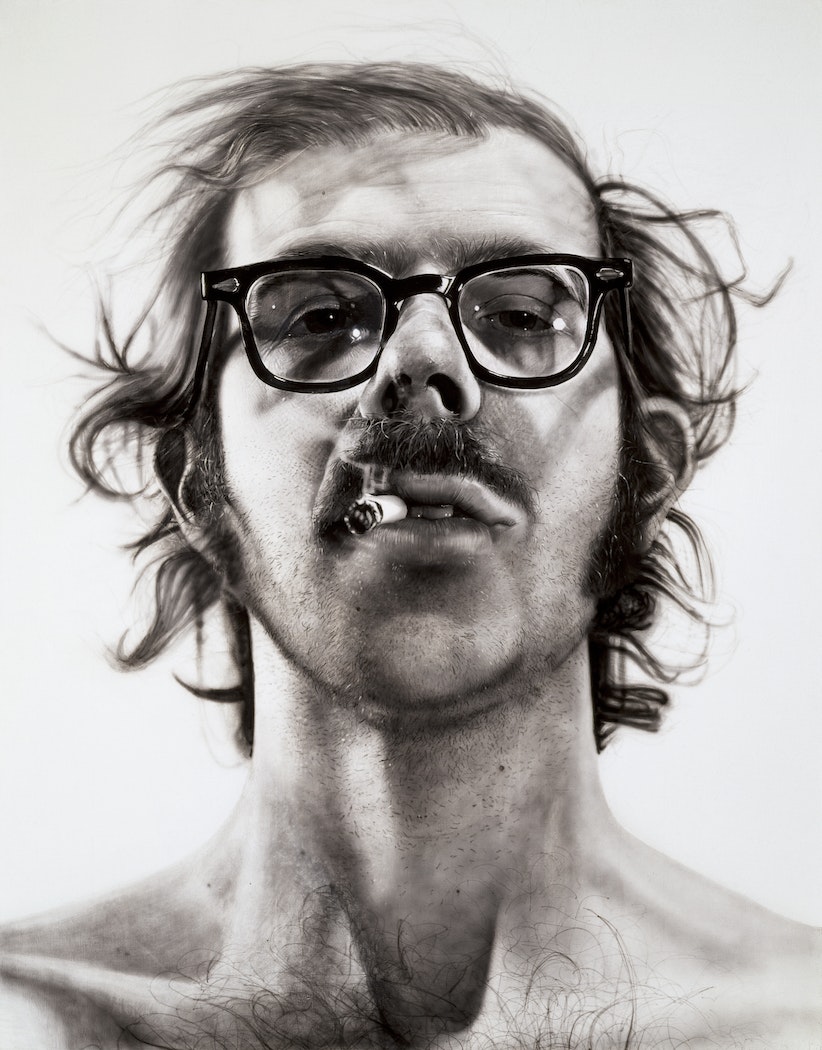

Big Self-Portrait (1967-1968) by Chuck Close
Tom Blackwell painted shop windows and gas engines as a symbol of freedom. Robert Bechtle portrayed various aspects of American society's daily life in his paintings. Richard Estes painted parts of New York skyscrapers. Ron Kleemann depicted large American trucks, Dan Eddy painted shiny metallic shields and automobiles, and Ralph Goings depicted fast-food restaurants alongside American cars of that era. Audrey Flack, the only female hyperrealist, painted a composition of cosmetics. Richard Estes focused on urban reflections along with geometric shapes.
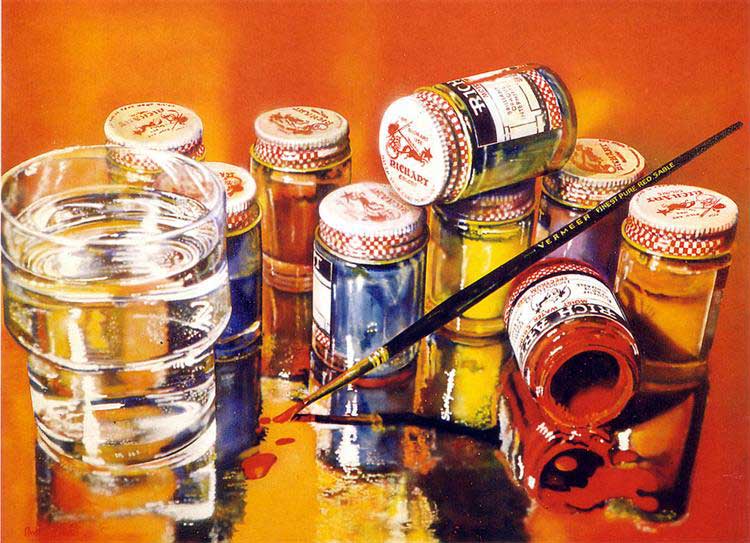

Audrey Flack hyperrealistic painting
Second Generation of Hyperrealist Painters
The second generation of hyperrealist painters emerged in the 1980s and 1990s. During this time, the efforts of the first generation had gained recognition and acceptance on a global scale, and the advancements in digital technology played a significant role in the artworks of these artists. The second-generation hyperrealists, especially, focused on displaying vast collections of skyscrapers and urban landscapes. Using a combination of wide-angled photography, Italian artist Anthony Brunelli expertly molded the subjects of his paintings, resulting in a compelling and thought-provoking series. Robert Gniewek painted rural areas at night, while Davis Cone depicted old cinemas. Rod Penner achieved notable precision and subtlety in showcasing details using powerful digital cameras.
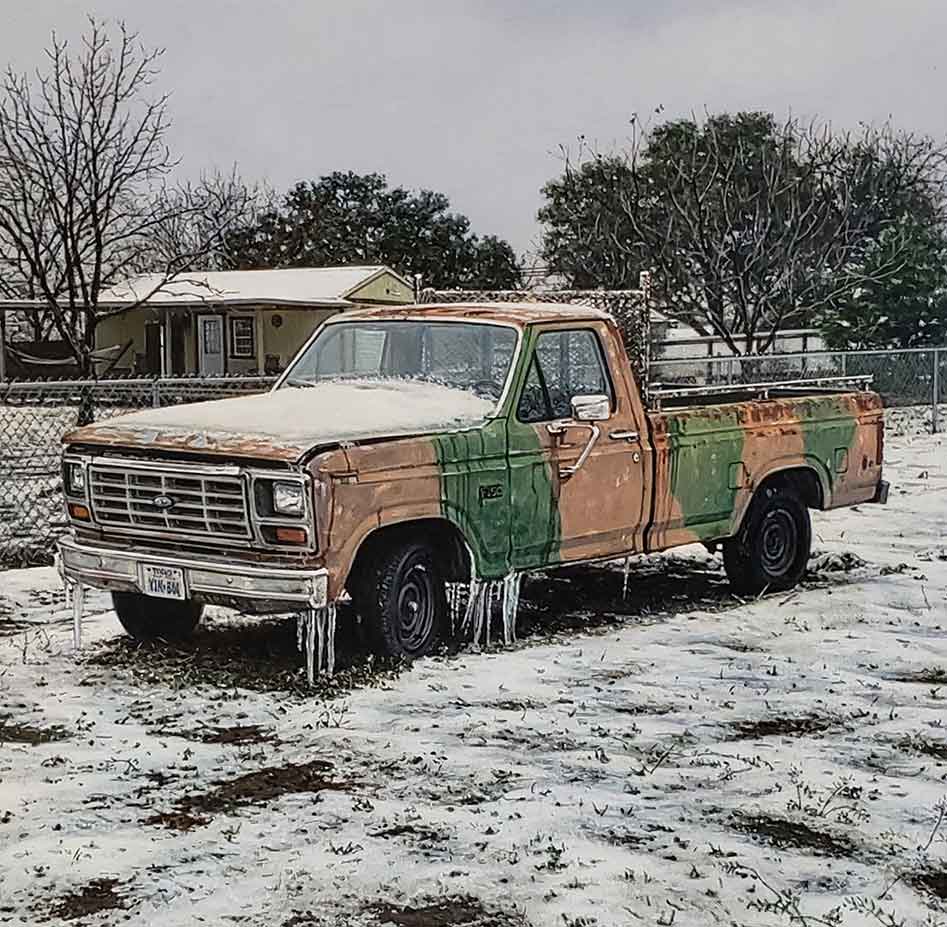

hyper realistic painting by Rod Penner
Subsequent Generations of Hyperrealist Painters
With the emergence of subsequent generations from the 1980s until now, the Hyperrealism movement has become an international style. Today's hyperrealists use modern photography tools to engage in photography and subsequently create more expansive and sophisticated hyper realistic paintings. Thanks to the transparency and high resolution offered by digital photos, these paintings have achieved an incredible level of life-like quality. Roberto Bernardi executes paintings of inanimate objects. Raffaela Spence paints the photographs she takes from the top of skyscrapers or inside helicopters. Now, many artists worldwide, after more than 70 years of the existence of Hyperrealism and advancements in its conceptual and artistic techniques, create a wide variety of hyper realistic paintings and designs.

Hyper realistic painting by Rod Penner
Nowadays, the mere mention of names like Dirk Dzimirsky, Diego Koy (also known as Diego Fazio), Denis Peterson, and Marco Grassi is enough to spark excitement among art enthusiasts. Hyperrealism has evolved into a dynamic and intricate genre, one that demands attention to its diverse nuances. Beyond replicating reality, this artistic style also conveys the individual viewpoints and interpretations of the talented creators behind it.
Characteristics of hyper realistic paintings
Hyperrealism is a style recognized for its outstanding sophistication and precision, a fact that cannot be overlooked. Its artists employ a multitude of techniques to achieve such mastery, including:
Using cameras to capture reality accurately
Using bright, vibrant colors
Using small, precise brushes
Subjects of hyper realistic paintings
Hyperrealistic paintings often feature commonplace subjects, such as human faces, industrial objects, and still lifes. These subjects are purposefully selected by artists to create visuals that strike a chord with viewers and induce a feeling of familiarity.
Hyperrealism and photography
Hyperrealism is remarkable for its uncanny resemblance to photography. In fact, some art experts go as far as labeling hyper realistic paintings as mere manual reproductions of photographs.
However, hyperrealist artists are firm in their belief that hyper realistic painting is not simply a replication of photography through hand-craftsmanship. To them, it goes beyond mere documentation of reality and encompasses the artist's own interpretation and unique viewpoint.
Hyperrealism and reality
Many people confuse hyperrealism for reality because of its incredible level of detail and precision. However, at its core, hyperrealistic painting is a unique and deliberate construction of reality. Each minute detail is carefully observed and meticulously rendered by the artist, capturing their own interpretation of the world around them.
Hyperrealism is a complex and multifaceted style that requires an understanding of its different aspects to appreciate. This style, in addition to recording reality, also expresses the artist's interpretation and perspective.